METHODS OF STOCK INVESTMENT
1. Initial Public Offer (IPO)
A company decides to go public to raise substantial amounts of capital by offering ownership interests in the company to the public at large. The first time going to public is called Initial Public Offering. Mostly securities offered in IPO include shares, bonds, Notes, limited partnership Units, and other types of investments in the company.
The highlights of an IPO may be:
- The company is never required to repay the capital, but instead the new shareholders have a right to future profits distributed by the company and the right to a capital distribution in case of dissolution
- In an IPO, the issuer may obtain the assistance of an underwriting firm, which helps it determine what type of security to issue (common or preferred), best offering price and time to bring it to market
- Underwriter also helps companies in case of under subscription of an IPO
- Company gives advertisements in the newspaper and Stock Exchange
- There are set rules to be followed while going public
- Banks are involved to distribute and collect subscription forms and payments on behalf of company
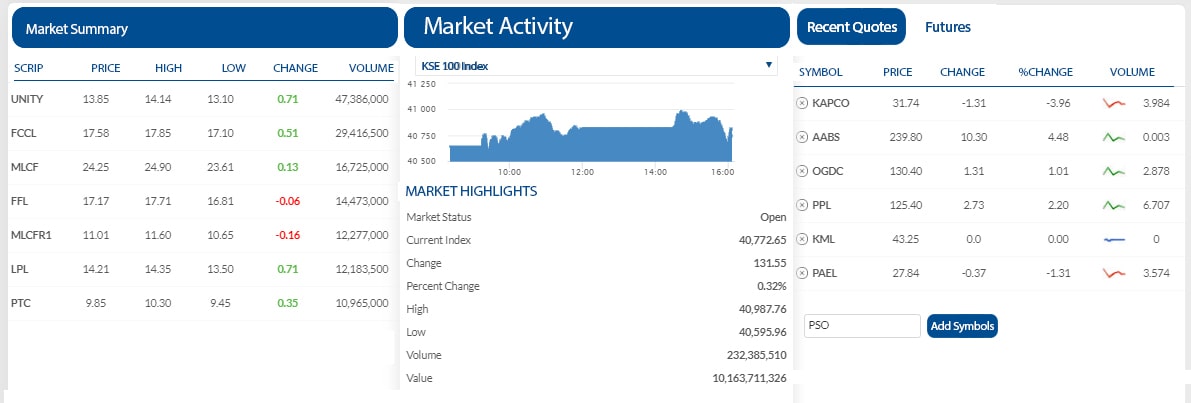
2. Secondary Market (Stock Exchange)
Secondary market can refer to the market for any kind of used goods. The market that exists in a new security just after the new issue is often referred to as the aftermarket. Once a newly issued stock is listed in a Stock Exchange, investors and speculators can easily trade in the exchange, as market makers provide bids and offers in the new stock. Liquidity is the main benefit of the secondary market. Secondary market is vital to an efficient and modern capital market. Fundamentally, secondary markets mesh the investor’s preference for liquidity.
A Stock Exchange or share market is a corporation or mutual organization which provides “trading” facilities for stock brokers and traders, to trade stocks and other securities. Stock Exchange also provides facilities for the issue and redemption of securities as well as other financial instruments and capital events including the payment of income and dividends. The securities traded on a Stock Exchange include: shares issued by companies, unit trusts and other pooled investment products and bonds.
Main features of Stock Exchange include:
- To be able to trade a security in a certain Stock Exchange, it has to be listed there
- All of the listed companies shares in a particular country or industry may increase or decrease in price because of rises and falls in economic confidence or changes in the particular industry
- Usually there is a central location at least for recordkeeping where physical shares are kept. (e.g: Central Depositary Company Pakistan)
- Trade on an exchange is allowed by members only (brokers)
- Supply and demand in stock markets are driven by various factors which, as in all free markets, affect the price of stocks
- There is usually no compulsion to issue stock via the Stock Exchange itself, nor must stock be subsequently traded on the exchange. Such trading is said to be off exchange or over-the-counter. This is the usual way that bonds are traded. Increasingly, Stock Exchanges are part of a global market for securities
- To Trade in the Stock Exchange, you must be an account holder with a member (broker) of an exchange